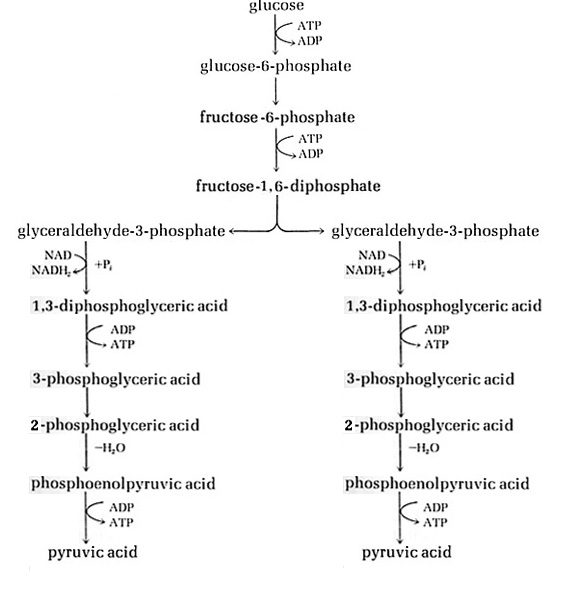
The Embden-Meyerhof PathwayThis is the pathway of glycolysis most familiar to biochemists and eucaryotic biologists, as well as to brewers, breadmakers and cheeseheads. The pathway is operated by Saccharomyces to produce ethanol and CO2. The pathway is used by the (homo)lactic acid bacteria to produce lactic acid, and it is used by many other bacteria to produce a variety of fatty acids, alcohols and gases. Some end products of Embden-Meyerhof fermentations are essential components of foods and beverages, and some are useful fuels and industrial solvents. Diagnostic microbiologists use bacterial fermentation profiles (e.g. testing an organism's ability to ferment certain sugars, or examining an organism's array of end products) in order to identify them, down to the genus level.
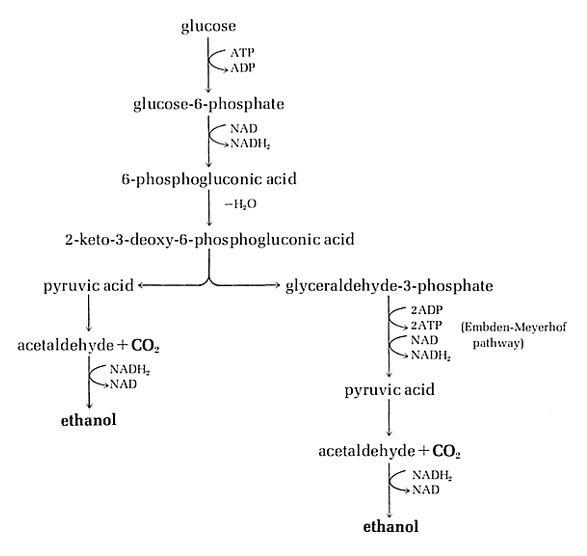
 The Entner-Doudoroff Pathway
The Entner-Doudoroff PathwayOnly a few bacteria, most notably Zymomonas, employ the Entner-Doudoroff pathway as a strictly fermentative way of life. However, many bacteria, especially those grouped around the pseudomonads, use the pathway as a way to degrade carbohydrates for respiratory metabolism (see Table 1 below). The E-D pathway yields 2 pyruvic acid from glucose (same as the E-M pathway) but like the phosphoketolase pathway, oxidation occurs before the cleavage, and the net energy yield is one mole of ATP per mole of glucose utilized.
In the E-D pathway, glucose phosphate is oxidized to 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconic acid (KDPG) which is cleaved by KDPG aldolase to pyruvate and GAP. The latter is oxidized to pyruvate by E-M enzymes wherein 2 ATP are produced by substrate level phosphorylations. Pyruvic acid from either branch of the pathway is reduced to ethanol and CO2, in the same manner as yeast, by the "yeast-like bacterium", Zymomonas (Figure below). Thus, the overall reaction is Glucose -->2 ethanol +2 CO2, and a net gain of 1 ATP.