|
|
| Subject |
Comments |
Views |
Author |
Date Written  |
|
How does our vision compare to some animals?
|
view preview
Do animals see the same way we do? Do some animals have better vision than humans? The senses of animals have evolved to give members of the species an optimum chance for survival. Here are a few examples: Some animals, such as cats, have a reflective surface ( tapetum) on the back of the eye behind the sensory receptors (left image above). When light first enters the eye, some light is detected by the sensory receptors. The light not detected by the sensory receptors continues onto the reflective surface at the back of the eye. This light is then reflected outward toward the sensory receptors, providing a second opportunity for detection. This feature produces two results. First, the outward reflection results in the shining of the cat's ey ...
|
|
|
0 |
14936 |
Biology Forums |
A year ago |
|
Memory-enhancing foods to help you study
|
view preview
There's more to studying than simply memorization and practice. It turns out that your diet also plays a pivotal role in recalling key bits of information, while keeping you energized and focused in the process. We're not talking about those scam-ridden supplements that promise a boost in brain power, but simple natural foods such as milk, nuts, seeds, rice, and oats. The nutrients found in these items help your study efforts by releasing natural memory enhancers called CCKs ( cholecystokinin). When CCK crosses the blood-brain barrier, it acts as a neurotransmitter associated with memory. Studies have shown that learning and memory processes are severely damaged (in rats) that genetically do not respond to the presence of CCK. And in people ...
|
|
|
1 |
20843 |
bio_man |
4 years ago |
|
Eyeless fish
|
view preview
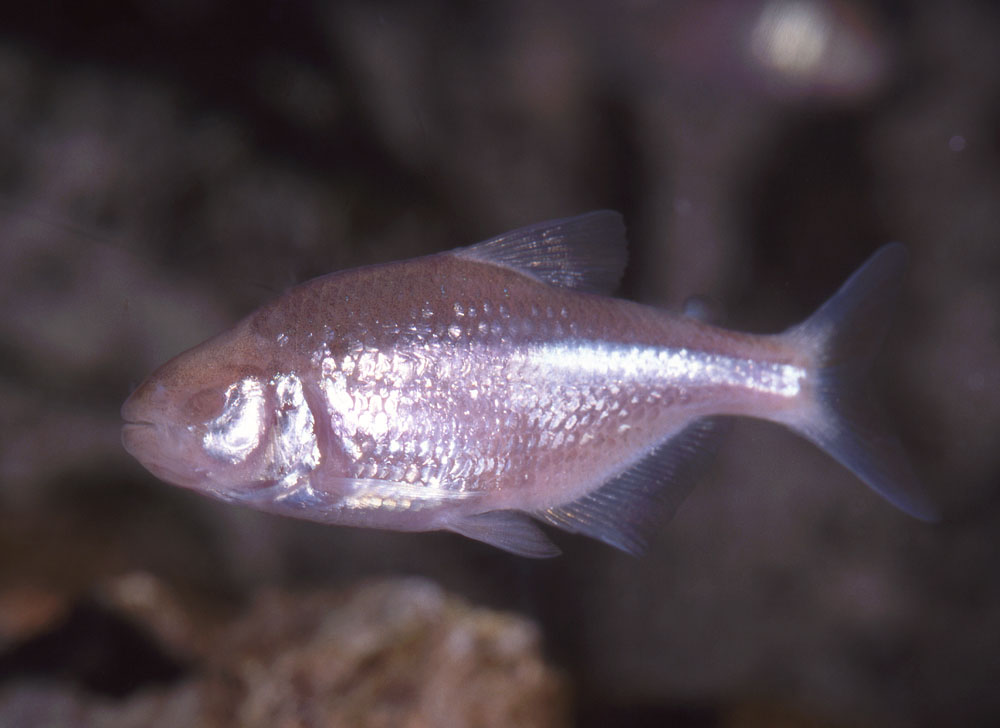 The Mexican tetra ( Astyanax mexicanus) is a blind, freshwater cave fish native to central and eastern parts of Mexico. Growing to a maximum total length of 12 cm (4.7 in), this species is notable for having no eyes or pigment; it has a pinkish-white color to its body (resembling an albino). The Mexican tetra spends most of its time in midlevel water above the rocky and sandy bottoms of pools and backwaters of creeks and rivers of its native environment. Coming from a subtropical climate, it prefers water with 6.5–8 pH and a temperature range of 20 to 25 °C (68 to 77 °F). In the winter, some populations migrates to warmer waters. Its natural diet consists of crustaceans, insects, and annelids. Given their peaceful nature, this species is popu ...
|
|
|
0 |
2361 |
bio_man |
5 years ago |
|
Time lapse of neural development
|
view preview
The video below shows 16 hours of neural development compressed into 40 seconds of a developing zebrafish's nervous system. Notice how the neurons branch to make connections with other neurons – a process vital to information transmission. To obtain such accurate footage, the animal's embryo was suspended in water, rather than gel, and its photographers used gentle light sheet technology to capture the specimen in 3D, at a high temporal resolution. ...
|
|
|
0 |
1239 |
bio_man |
5 years ago |
|
What does a box and these fish have in common?
|
view preview
Their name and shape!Ostraciidae is a family of squared, bony fish closely related to the pufferfishes and filefishes. Members of this family occur in a variety of different colors (e.g. right - Hawaiian Blue Boxfish, Ostracion meleagris and the Yellow Boxfish, Ostracion cubicus), and are notable for the hexagonal or "honeycomb" patterns on their skin. Boxfish swim in a rowing manner. Their hexagonal plate-like scales are fused together into a solid, triangular or box-like carapace, from which the fins, tail, eyes and mouth protrude. Because of these heavy armoured scales, Ostraciidae are limited to slow movements, but few other fish are able to eat the adults. Some boxfish also secrete poisons from their skin into the surrounding water, fu ...
|
|
|
0 |
6159 |
bio_man |
6 years ago |
|
One hairy situation
|
view preview
The hairy frogfish ( Antennarius striatus) is a marine fish with spines resembling strands of hair - and it can change color. This small fish grows up to 22 cm (8.7 in) long, and has a rounded, extensible body. Its large mouth is forwardly extensible, allowing it to swallow prey as large as itself! The coloring of its body is extremely variable because individual fish tend to match their living environments. Frogfishes have the capacity to change coloration and pigment pattern, taking only a few weeks to adapt. The dominant coloration varies from yellow to brownish-orange, passing through a range of shades, but it can also be green, gray, brown, almost white, or even completely black without any pattern. Body and fins can be marked with roug ...
|
|
|
0 |
7174 |
duddy |
7 years ago |
|
|
2 |
4878 |
duddy |
7 years ago |
|
The ghost fish has been captured on video for the first time
|
view preview
A living, swimming ghost fish has been seen live for the first time ever. The fish, part of the family Aphyonidae, was caught on camera during an ongoing National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) exploration by the ship Okeanos Explorer. The exploration centers on the deep ocean at Mariana Trench Marine National Monument, a protected area spanning 95,216 square miles (246,608 square kilometers) east of the Philippines. The secretive fish was swimming along a ridge 8,202 feet (2,500 meters) down, according to NOAA. The animal is about 4 inches (10 centimeters) long, with translucent, scale-less skin and eerie, colorless eyes. No fish in the family Aphyonidae has ever been seen alive before. ...
|
|
|
1 |
4958 |
duddy |
7 years ago |
|
What do elephants and fish have in common?
|
view preview
Nothing, except for this fish, appropriately named the elephantnose fish ( Gnathonemus petersii) for its peculiar, elongated spout. The fish is widespread in the flowing waters of West Africa and hunts insect larva at dawn and dusk. Its nose is actually a sensitive extension of its mouth, that it uses for self-defense, communication, navigation, and finding worms and insects to eat. This organ is covered in electroreceptors, as is much of the rest of its body. The elephantnose uses a weak electric field, which it generates with specialized cells called electrocytes, which evolved from muscle cells, to find food, to navigate in dark or turbid waters, and to find a mate. The elephantnose fish live to about 6 to 10 years. ...
|
|
|
2 |
5504 |
duddy |
7 years ago |
|
Parrotfish make a cocoon of mucus and wrap themselves like a sleeping bag each night
|
view preview
Gnathiids are a family of isopod crustaceans whose larvae feed on the blood of fish. During the day, infected parrotfish seek out cleaner fish to consume the parasites; however, at night they are relatively vulnerable to attack. Parrotfish overcome this vulnerability by secreting a mucus cocoon before sleeping which envelopes their bodies with a protective biopolymer that functions similar to a mosquito net. The mucus is secreted from large glands in the gill cavity and is composed of small glycoproteins which are extensively cross-linked through pyrosulfate bonds. This exopolymer net allows small molecules to permeate but prevents the parasitic gnathiids from entering. The process is thought to involve a combination of blocking odorants ...
|
|
|
1 |
4954 |
duddy |
8 years ago |
|
This baby fish will grow up to be one of the fastest fish in the sea
|
view preview
While it may look small now, this baby swordfish ( Xiphias gladius) grows fast and can reach 14 feet in length and weigh up to 1,200 pounds as an adult. They are found in the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian oceans and sometimes cold waters, including the Mediterranean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, the Black Sea, and the Sea of Azov. They are highly migratory, moving to warmer waters in the winter and cooler waters in the summer. While they are not at the top of the food chain, it is not a fish to be messed with; apparently, even sharks are wary of them! ...
|
|
|
4 |
17624 |
duddy |
8 years ago |
|
Piranhas, meet your match
|
view preview
Shown above are vampire fish caught in Corona Falls, Guyana. Also called payara by locals, these Amazon Basin predators feed on other fish, especially piranhas, which they impale on their long fangs.
|
|
|
0 |
6539 |
duddy |
8 years ago |
|
What some fish will do to survive
|
view preview
Shallow waters will sometimes get too hot, forcing one fish to make a break for the shore. The tiny mangrove rivulus (shown above) avoids neurological damage from hot swamps by escaping to land. Retreating to land allows the fish to cool down through a process called evaporative cooling, which is akin to human sweating but using water from the environment. Previously, scientists had suggested that the fish, besides simply escaping hot water, might be taking advantage of evaporative cooling. Source: http://rsbl.royalsocietypublishing.org/content/11/10/20150689 ...
|
|
|
0 |
20476 |
duddy |
8 years ago |
|
Turns out that fish oil only benefits those who have the right genes
|
view preview
Most foods today are fortified with essential oils like omega-3 fatty acids. Naturally, these oils are found in fish, and are known to benefit many parts of the body, including the eyes, brain, heart, and joints. So, are these so-called beneficial oils important for people who lack the DNA profile needed to metabolise them? It turns out that the extra omega-3 might not do much good at all. According to a study published in Science, Inuit people living in Greenland whose traditional diet of fish and marine mammals have the right enzymes in their bodies needed to metabolise these foods that are very high fat content. The researchers reported that their DNA that was most different was on chromosome 11, specifically among genes that control the ...
|
|
|
0 |
15458 |
duddy |
8 years ago |
|
Coolest elevator ride ever
|
view preview
The AquaDom is a 25 m (82 ft) tall cylindrical acrylic glass aquarium built at the Radisson Blu Hotel in Berlin, Germany. You can ride the transparent elevator it has in the center!
|
|
|
3 |
4214 |
duddy |
8 years ago |
|