Definition for Difference between revisions of "Pyrimidine"
From Biology Forums Dictionary
(Created page with "The bases cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U) with a single ring.") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | The bases cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U) with a single ring. | + | 1) The bases cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U) with a single ring. |
| + | |||
| + | 2) In organic chemistry, pyrimidine is an aromatic, nitrogen-containing six-membered ring compound. | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://guweb2.gonzaga.edu/faculty/cronk/biochem/images/pyrimidines.gif | ||
| + | |||
| + | In biochemistry, pyrimidine is understood usually as a generic term for heterocyclic bases - components of nucleotides and nucleic acids - that contain the pyrimidine structure as a nucleus (compare with purines). Thus, the three pyrimidine bases shown in the figure - cytosine (2-oxo, 4-amino pyrimidine), uracil (2,4-dioxopyrimidine), and thymine (2,4-dioxo-5-methylpyrimidine or 5-methyluracil) - are the standard pyrimidine bases found in DNA and RNA. Thymine is usually limited to DNA, while in RNA uracil takes the place of thymine. | ||
Latest revision as of 15:39, 10 December 2011
1) The bases cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U) with a single ring.
2) In organic chemistry, pyrimidine is an aromatic, nitrogen-containing six-membered ring compound.
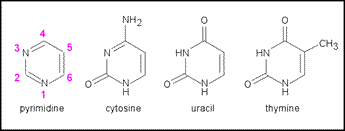
In biochemistry, pyrimidine is understood usually as a generic term for heterocyclic bases - components of nucleotides and nucleic acids - that contain the pyrimidine structure as a nucleus (compare with purines). Thus, the three pyrimidine bases shown in the figure - cytosine (2-oxo, 4-amino pyrimidine), uracil (2,4-dioxopyrimidine), and thymine (2,4-dioxo-5-methylpyrimidine or 5-methyluracil) - are the standard pyrimidine bases found in DNA and RNA. Thymine is usually limited to DNA, while in RNA uracil takes the place of thymine.
