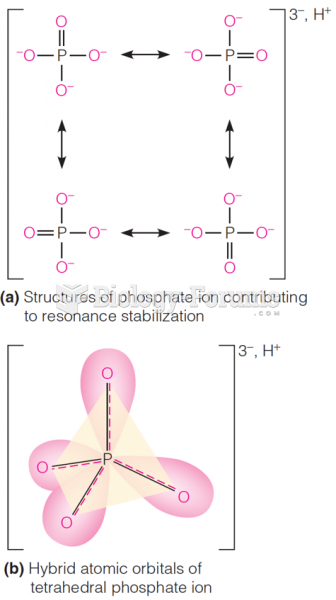
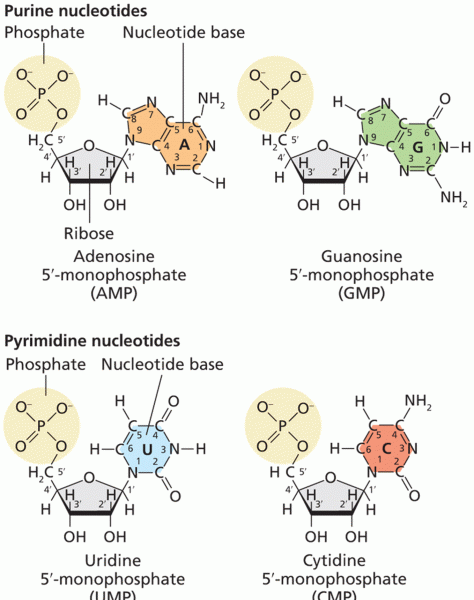
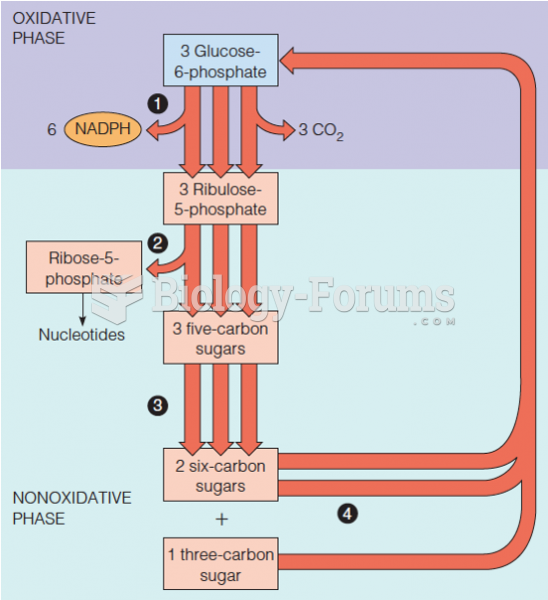
Definition for Pyridoxal phosphate
From Biology Forums Dictionary
An important cofactor that functions in a wide variety of enzyme-catalyzed reactions. Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) is derived from pyridoxine (vitamin B6). PLP is an especially important cofactor in reactions of amino acid metabolism.
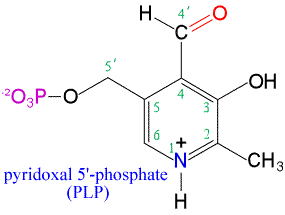
Among the biochemical reactions in which PLP participates are: transamination, decarboxylation, deamination, racemization, aldol cleavage reactions, as well as eliminations and replacements at the b and g atoms of amino acid side chains. In all these reactions, PLP forms Schiff base intermediates (via the 4' aldehyde group - red in figure at left) and is able to act as an electron sink. The pyridine ring nitrogen (N1, blue in figure) assists in this respect by attracting electrons to neutralize its formal charge of +1. PLP also functions in the phosphorolytic cleavage of glycogen, although its mode of action (the 5' phosphate acts as a general acid-base catalyst) in this case is completely different from that in the above reactions.