Definition for Fluorescence resonance energy transfer
From Biology Forums Dictionary
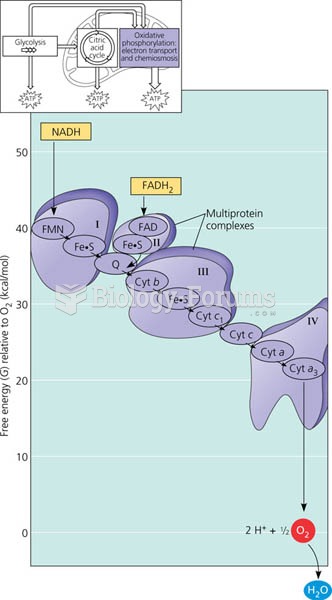
Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) is a distance-dependent interaction between the electronic excited states of two dye molecules in which excitation is transferred from a donor molecule to an acceptor molecule without emission of a photon. The efficiency of FRET is dependent on the inverse sixth power of the intermolecular separation, making it useful over distances comparable to the dimensions of biological macromolecules. Thus, FRET is an important technique for investigating a variety of biological phenomena that produce changes in molecular proximity. When FRET is used as a contrast mechanism, colocalization of proteins and other molecules can be imaged with spatial resolution beyond the limits of conventional optical microscopy.