Definition for Acetyl-CoA carboxylase
From Biology Forums Dictionary
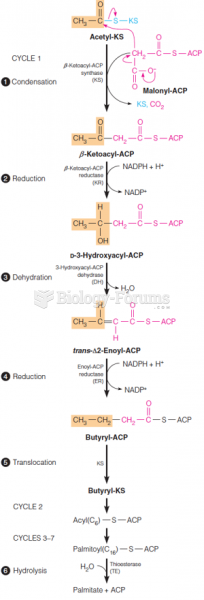
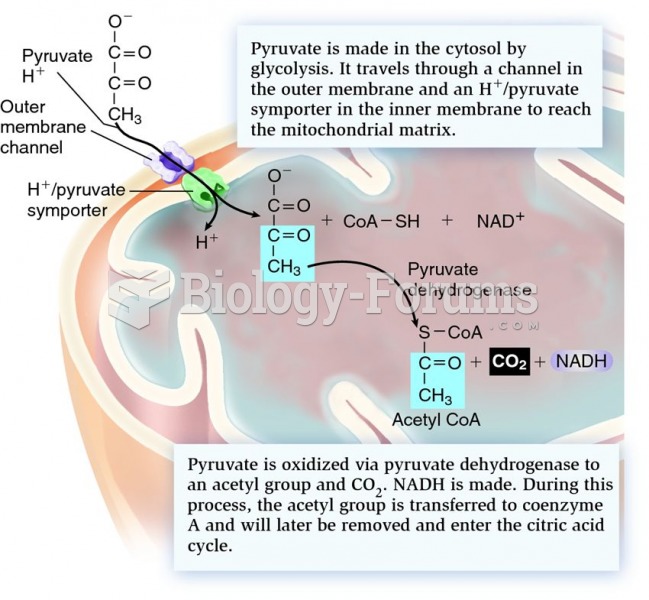
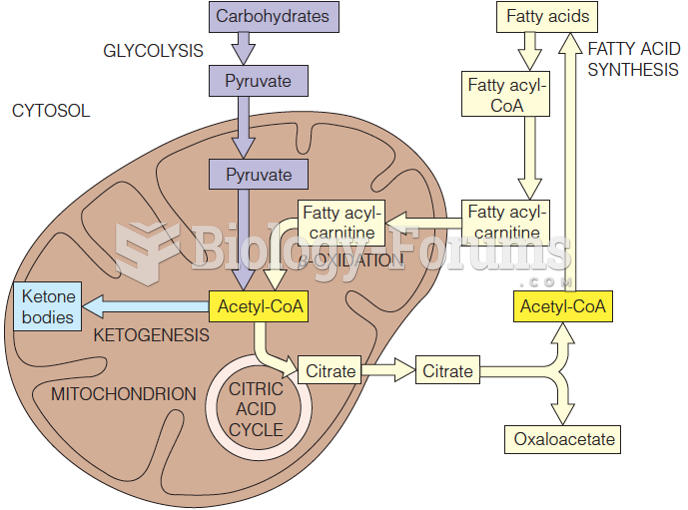
Acetyl CoA carboxylase is an enzyme catalyzing the initial, committed step of fatty acid synthesis. ACC, which employs a biotin cofactor, transfers an activated CO2 group (derived from bicarbonate) to acetyl CoA, forming malonyl CoA. This reaction requires the input of free energy from ATP hydrolysis to make it energetically favorable. The chemical equation for the reaction catalyzed by ACC is as follows:
ATP + acetyl CoA + HCO(3)(-) <=> ADP + phosphate + malonyl-CoA.
Since ACC catalyzes the committed step of the fatty acid synthetic pathway, it is highly regulated. High levels of fatty acyl-CoA or AMP and conditions that activate protein kinase A typically inhibit ACC. Insulin and high levels of citrate typically activate ACC.