Definition for Marfan
From Biology Forums Dictionary
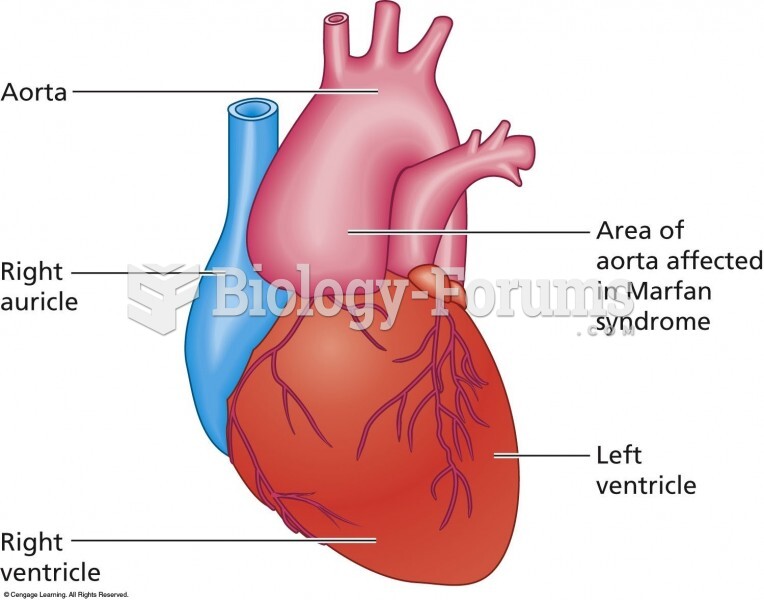
Marfan’s syndrome (MFS) is one of the most common autosomal dominant inherited disorders of connective tissue, affecting the heart (aortic aneurysm and dissection, mitral valve prolapse), eye (dislocated lenses, retinal detachment) and skeleton (tall, thin body build with long arms, legs and fingers; scoliosis and pectus deformity).
Clinically, two of three major systems must be affected, to avoid overdiagnosing the condition. Diagnosis may be confirmed by studying family linkage to the causative gene, or by demonstrating a mutation in the Marfan’s syndrome gene (MFS1) for fibrillin (FBN-1) on chromosome 15q21. MFS affects approximately 1 in 5000 population worldwide and 25% of patients are affected as a result of a new mutation. This group includes many of the more severely
affected patients, with high cardiovascular risk. Other known associations with early death due to aortic aneurysm and dissection are: family history of early cardiac involvement; family history of dissection with an aortic root diameter of > 5 cm; male sex; and extreme physical characteristics, including markedly excessive stature and widespread striae. Histological examination of aortas often shows widespread medial degeneration, described as ‘cystic medial necrosis’.