Definition for Renal threshold of glucose (RTG)
From Biology Forums Dictionary
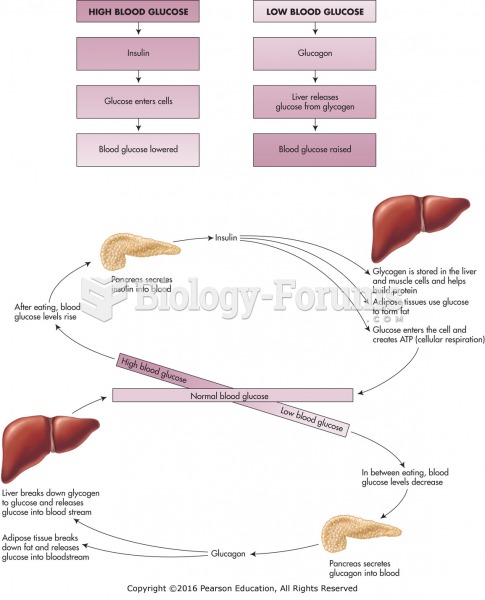
The Renal threshold of Glucose (RTG) is the blood glucose concentration at which glucose begins to be excreted by the kidneys into the urine. This usually occurs in healthy adults at approximately 9 - 10 mmol/L (162 - 180 mg/dL).
In many adults, particularly those with long-standing diabetes, the RTG may increase substantially. Thus, raised blood glucose levels may exist without glucose being detected in the urine. Conversely, some individuals, particularly children and pregnant women, may have very low or variable renal thresholds for glucose, resulting in glucose being present in the urine, even with normal blood glucose values.
The values used by AIDA on-line for the Renal threshold of glucose (RTG) are:
- Low = 7 mmol/L (126 mg/dL)
- Normal = 9 mmol/L (162 md/dL)
- High = 11 mmol/L (198 mg/dL)