Definition for Serine
From Biology Forums Dictionary
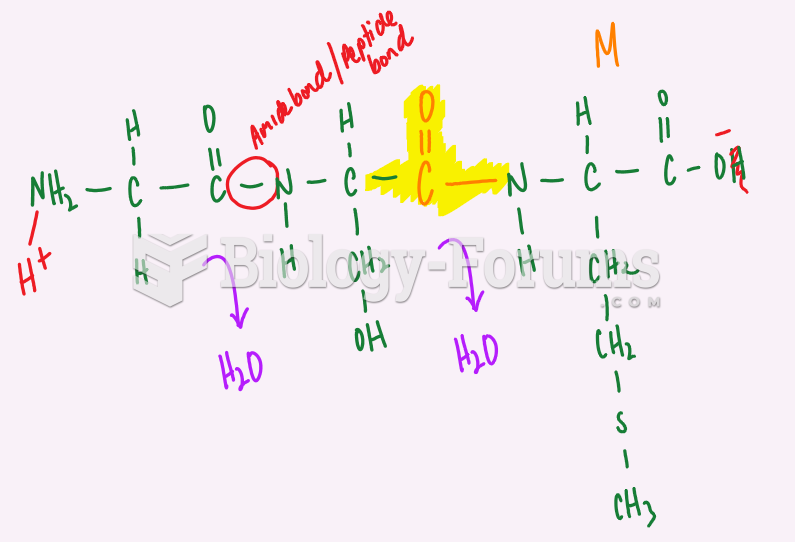
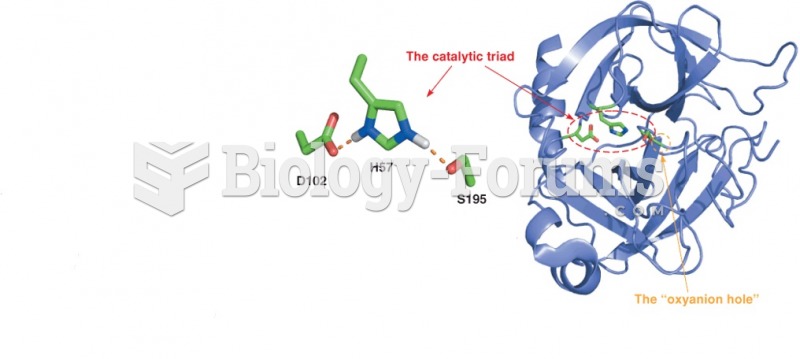
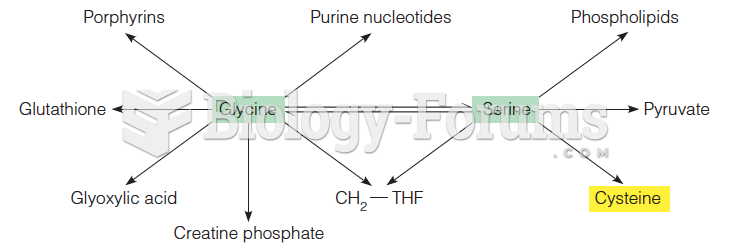
One of the standard set of 20 amino acids. The side chain of serine is chemically equivalent to a substituted methanol. The hydroxyl group of the serine side chain can act as a hydrogen bond donor or acceptor, and has nucleophilic character. The latter property is utilized by the serine proteases, a class of proteolytic enzymes that includes trypsin, chymotrypsin, and subtilisin. Serine is one of the most frequently modified residues in proteins by post-translational phosphorylation - attachment of a phosphate group - of the side chain hydroxyl. Other residues commonly modified in this way are the other hydroxyl-containing amino acids threonine and tyrosine. The hydroxyl group of serine residues in proteins also often serves as a point of attachment for carbohydrate moieties, a post-translational modification termed O-glycosylation. In the case of serine and threonine, the proximal O-linked sugar is usually N-acetylgalactosamine, which is typically attached to proteins passing through the Golgi apparatus. Serine is also involved in lipid biochemistry, as its hydroxyl group is found esterified to phosphatidic acid in phosphatidylserine, a common phosphoglyceride.
Codons UCN, AGU, AGC. (Serine is one of three amino acids with six codons - the others are arginine and leucine.)
Symbols: Ser, S.