Definition for Urea cycle
From Biology Forums Dictionary
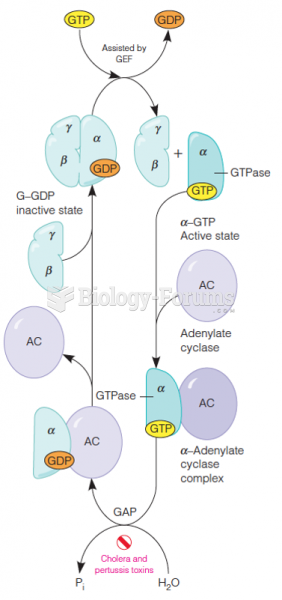
The metabolic pathway [diagram] by which most terrestrial vertebrates excrete nitrogen derived from amino acid catabolism. In the urea cycle, amino groups of urea are donated by carbamoyl phosphate and aspartate, while the carbon atom of urea is contributed by bicarbonate.
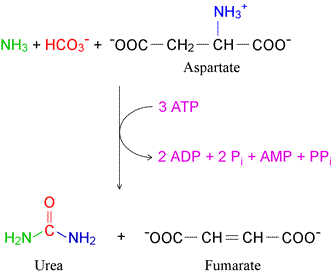
The net equation of the urea cycle, shown at left, includes the production of fumarate, as well as the consumption of four "high energy" phosphoanhydride bonds, contributed by ATP. Two of these are used by for synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate from bicarbonate and ammonia, carried out by carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I. The other energy-requiring step is the joining of aspartate via its a-amino group to citrulline in a reaction catalyzed by argininosuccinate synthetase [EC 6.3.4.5], which also releases pyrophosphate (PPi). The latter is hydrolyzed, helping to drive the urea cycle in favor of urea production. Urea is secreted into the bloodstream, from which it is ultimately eliminated by the kidneys for excretion. The amino acid arginine is an intermediate in the urea cycle