Definition for Signal peptide
From Biology Forums Dictionary
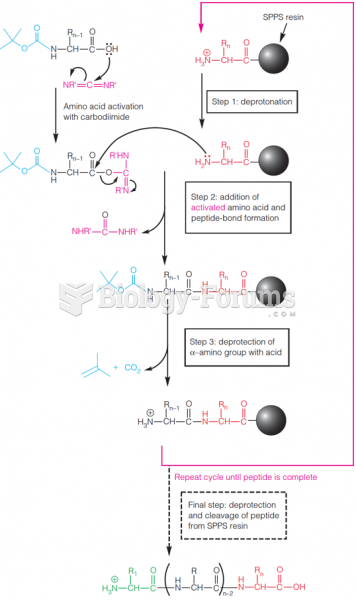
A signal peptide is a short peptide (usually 16-30 amino acids long) present at the N-terminus of the majority of newly synthesized proteins that are destined towards the secretory pathway. These proteins include those that reside either inside certain organelles (the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi or endosomes), secreted from the cell, or inserted into most cellular membranes. Although most type I membrane-bound proteins have signal peptides, the majority of type II and multi-spanning membrane-bound proteins are targeted to the secretory pathway by their first transmembrane domain, which biochemically resembles a signal sequence except that it is not cleaved. They are a kind of target peptide.