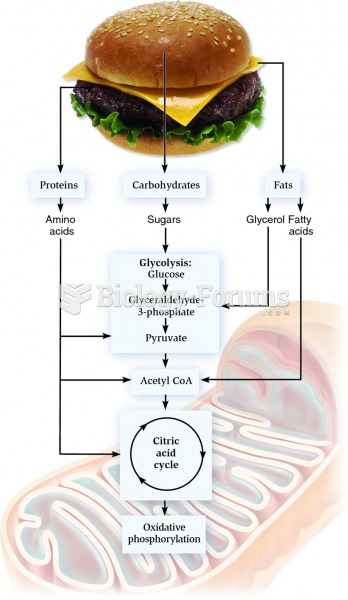
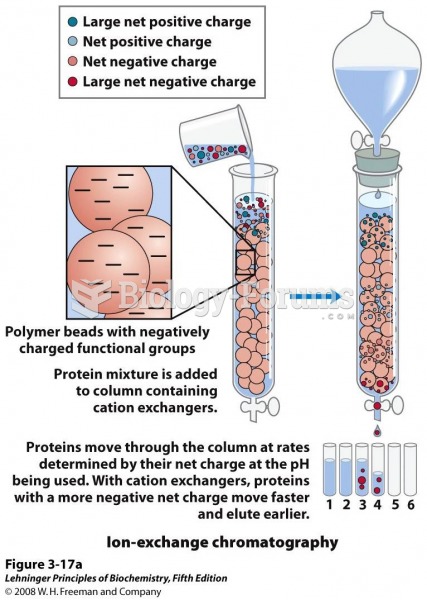
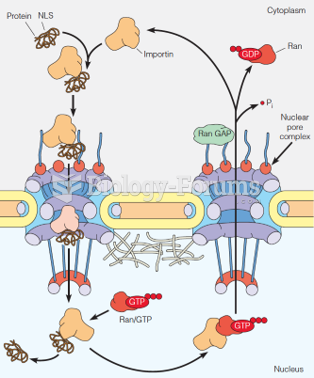
Definition for Rho protein
From Biology Forums Dictionary
Rho protein functions as a hexamer of a single polypeptide chain with 419 residues, which is the product of the rho gene. It is an RNA-binding protein with the capacity to hydrolyze ATP and other nucleoside triphosphates. Rho acts to cause termination by first binding to a site on the nascent transcript from the transcription holoenzyme and by subsequently using its ATP hydrolysis activity as a source of energy to mediate dissociation of the transcript from RNA polymerase and the DNA template.
Its six identical subunits are arranged in a torus with six canonical ATP binding sites located at the interfaces of the C-terminal domains of adjacent subunits. Each ATP binding site is composed of adjacent Walker-A/Walker-B motifs typical of RecA-like proteins that utilize NTP to perform mechanical work in the cell After binding to a transcript at a cytosine-rich rut (Rho utilization) site, Rho loads the polynucleotide into its central channel before adopting a conformation competent to processively translocate along the strand.