Definition for Synthesis-dependent strand annealing
From Biology Forums Dictionary
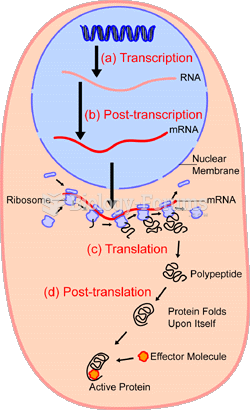
Synthesis-dependent strand annealing (SDSA) is an error-free process that repairs double-strand breaks occurring after the completion of DNA replication. When a double-stranded break (DSB) affects one sister chromatid; the other chromatid is intact. The strand invasion process displaces one strand of the duplex and creates a displacement (D) loop. DNA replication within the D loop synthesizes new DNA strands from intact template strands, and the sister chromatids are reformed by dissociation and annealing of the nascent strand to the other side of the break. By accomplishing the removal of DNA in the immediate vicinity of a double-stranded break and the replacement of the excised DNA with a duplex identical to that in the sister chromatid, SDSA carries out error-free repair of double-stranded breaks.