Definition for Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
From Biology Forums Dictionary
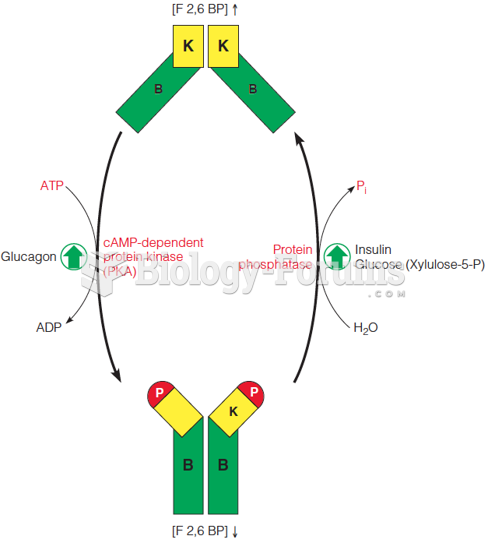
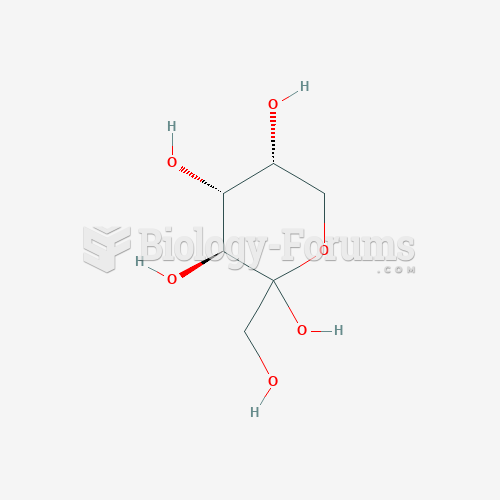
A six-carbon phoshosugar, which is an intermediate in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (FBP) is a bisphosphate ester of fructose. (The "bis" prefix denotes that two different hydroxyl groups are phosphorylated.) Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is produced in glycolysis by the enzyme phosphofructokinase, which acts on the substrate fructose 6-phosphate. FBP exists as a cyclic hemiacetal, in the form of a five-membered furanose ring. In the next step of glycolysis, this ring is opened and FBP is cleaved into two three-carbon phosphosugars, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (GAP) and dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP). This transformation is reversibly catalyzed by aldolase, which is an enzyme of both glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. In gluconeogenesis, FBP is hydrolyzed to fructose 6-phosphate by the enzyme fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase), which, along with phosphofructokinase, is highly regulated.