The field of biology is a fascinating and diverse one, one which has seen a great many groundbreaking discovery over the years. Here are 5 famous biologists and their discoveries that helped shape our world today.
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek – known as the father of microbiology 1632–1723
1632–1723 Leeuwenhoek is well known for his contributions to microscopy, and how he applied this to the field of biology. He revolutionised a technique for creating powerful lenses, which some speculate were able to magnify up to 500 times. Leeuwenhoek used the microscopes to find out more about the living world – his discoveries include bacteria, the vacuole of the cell, and the banded pattern of muscle fibres.
Robert Hooke – famous for discovering the cell 1635 – 1703
1635 – 1703 Hooke was primarily a physics and chemistry specialist but his discovery of the cell has been monumentally impactful on the world of biology. Hooke had an extraordinary ability to manipulate microscopes, and when applying this ability to looking closely at a thin slice of cork observed empty spaces contained with walls - terming them cells. We now know that cells are the building blocks of all life.
Carl Linnaeus – known as the father of modern taxonomy 1707–1775
1707–1775 A botanist, physician and zoologist all at the same time, Linnaeus came up with the system of naming, ranking, and classifying organisms that we still use today. It was his vast collection of specimens of plants, animals, and shells that lead to Linnaeus' coming up with a way of grouping and naming species. He separated all living things into 3 kingdoms; animals, plants and minerals, subdividing them into classes, then into orders and then finally into genera and species. You've heard of Homo sapiens right? Homo is the genus and sapiens the species – as you can see still very much in use today.
Charles Darwin – famous for the theory of evolution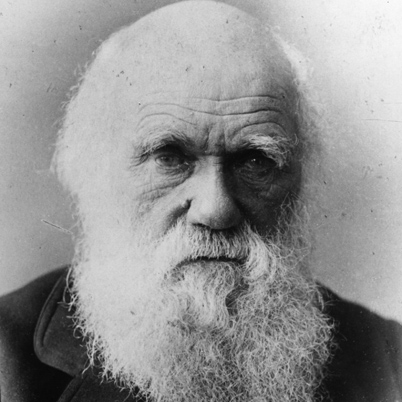 1809–1882
1809–1882 Probably the most famous naturalist of all time, Darwin's contribution to biology and society is beyond imagination. He established that all species of life have descended over time from common ancestors, the existence of new species occurring via the process of natural selection. His theory of evolution was published in On the Origin of Species in 1859 and it caused quite the stir – Darwin was disputing the longheld belief that all species had been created by God at the beginning of the world. Evolution by natural selection combined with Mendelian genetics is now accepted as the modern evolutionary synthesis and forms the foundations of much biological scientific endeavour.
Gregor Mendel – the founder of modern genetics 1822–1884
1822–1884 Mendel's extraordinary contribution didn't receive its just recognition until long after the friar's death – you could call him the Van Gogh of the biological world. Mendel used peas to discover and demonstrate the laws of genetic inheritance, coining the terms dominant and recessive genes in the process. The laws were rediscovered at the turn of the 20th century and provided the mechanism by which Darwin's theory of natural selection can occur. The two theories combine to form our current understanding of the evolutionary process.